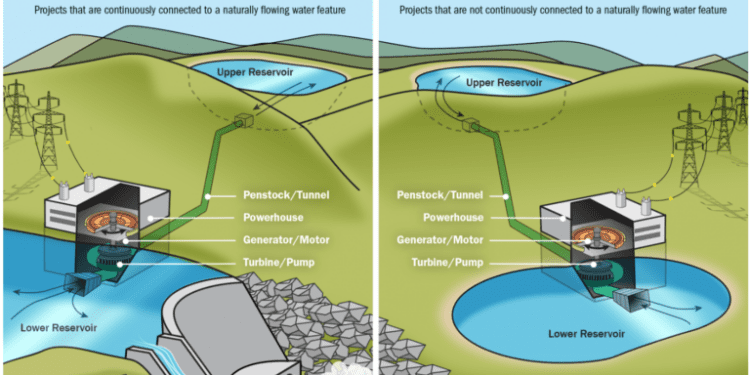
India is taking steps to better integrate renewable energy capacity into its grid. The Ministry of Power has issued draft guidelines to procure power from pumped hydro storage projects, with the goal of setting up 18 gigawatts of capacity. This form of storage works by pumping water from a reservoir at a lower elevation to another at higher elevation, using low cost renewable power during periods of low demand and high generation. Currently, India has 8 gigawatts of pumped hydro storage projects, with 4 more under construction and 26 allocated to states. The Central Electricity Authority estimates that India will need 18.8 gigawatts of pumped hydro storage and 51.5 gigawatts of five-hour battery storage to meet its 500 gigawatt renewable energy target by 2032.
Greenko Energy has been leading the way in developing pumped storage projects in India, and has tied up with industrial groups to supply round-the-clock renewable energy. While battery storage is more flexible in response time and applications, pumped hydro is a tested technology with little to no dependence on imports.
The move towards pumped hydro storage is a positive step for India’s renewable energy sector, as it will help to better integrate renewable energy capacity into the grid. It is also a great example of how businesses can work together to create a more sustainable future. With the right incentives and support, India can continue to make strides towards a greener future.
FAQ
Q1. How electric car batteries work?
A1. Electric car batteries are typically lithium-ion batteries that store energy and power the motor. They are recharged by plugging the car into an electric outlet or charging station.
Q2. What electric car has the longest range?
A2. The Tesla Model S has the longest range of any electric car currently on the market, with a range of up to 370 miles on a single charge.
Q3. How electric car batteries are recycled?
A3. Electric car batteries are recycled by breaking them down into their component parts and then separating out the metals, plastics, and other materials for reuse. The metals are melted down and reused in new products, while the plastics and other materials are recycled into new products.