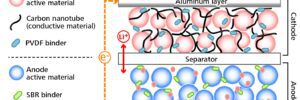
Chinese battery-maker CATL has chosen to use Japan-based Toyocolor‘s Lioaccum conductive carbon nanotube (CNT) dispersion for its high-capacity Li-ion batteries. The batteries, which will be installed in mass-produced vehicles beginning in 2024, are expected to provide superior conductive performance and expanded capacity and energy density.
Toyocolor’s CNT dispersion is designed to replace conventional carbon black as the conductive material in battery cathodes. This substitution is expected to result in improved conductivity with a nominal amount of material. To meet CATL’s supply needs, Toyocolor will be expanding the capacity of its dispersion production base, Zhuhai Toyocolor, in Guangdong, China.
The use of Toyocolor’s CNT dispersion is expected to revolutionize the automotive industry by providing high-capacity Li-ion batteries that are more efficient and reliable than ever before. This technology could potentially lead to longer-lasting batteries and improved performance for electric vehicles. CATL’s decision to use Toyocolor’s CNT dispersion is a major step forward in the development of advanced battery technology.
FAQ
Q1: Are electric car batteries recyclable?
A1: Yes, electric car batteries are recyclable.
Q2: Are electric car chargers free?
A2: It depends on the charger and the location. Some electric car chargers are free, while others may require a fee.
Q3: Can electric car batteries be rebuilt?
A3: Yes, electric car batteries can be rebuilt with the right tools and knowledge.