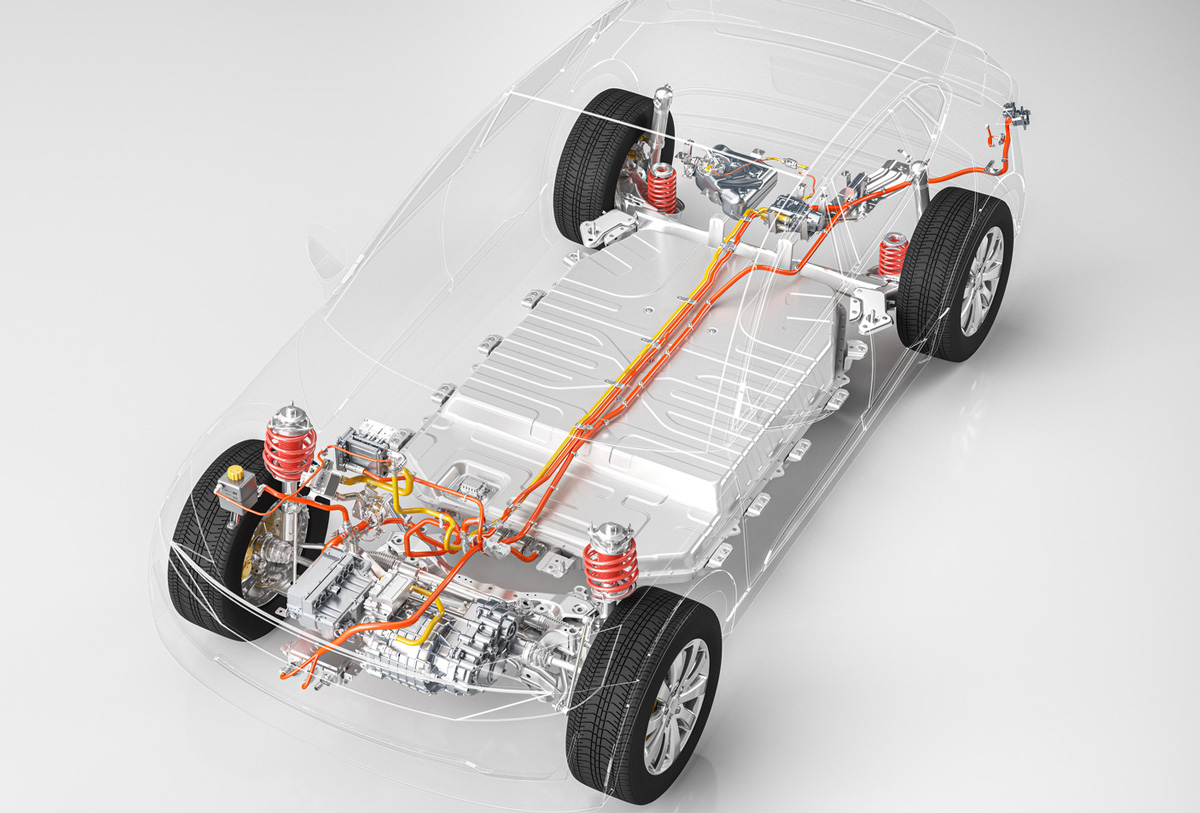



Automotive electrification significantly impacts testing methods, encompassing areas such as:
- Powertrain testing procedures – Engineers now focus on battery chemistry, inverter logic, and motor rotor positioning rather than traditional methods of measuring fuel consumption and emissions.
- Environmental and thermal testing – Manufacturers must simulate extreme weather conditions for high-voltage battery systems, making temperature and moisture sensitivity a crucial factor.
- Noise and vibration testing – With electric vehicles, the absence of internal combustion engine noise makes NVH testing increasingly vital. Engineers must now pay closer attention to detecting motor-related issues.
- EMC testing – Compliance with FCC standards for Electromechanical Component testing is mandatory due to the electric nature of BEVs, raising the importance of addressing potential electromagnetic emissions from the vehicle and electric motor.
Read this overview to learn about designing facilities and infrastructure, unique safety challenges, customization options, and electrification application examples.









