The U.S. solar market experienced a 16% decrease in new solar capacity additions in 2022, according to the U.S. Solar Market Insight 2022 Year in Review released today by the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) and Wood Mackenzie. This was due in large part to an investigation into new anti-circumvention tariffs by the U.S. Department of Commerce, as well as equipment detainments by Customs and Border Protection under the Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act. Despite this, the report features updated 10-year baseline forecasts, along with high and low deployment scenarios based on solar module supply and domestic manufacturing, Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) guidance and sector-specific factors such as labor availability, tax equity supply and interconnection timelines.
The residential solar market experienced a 40% increase in installed solar capacity in 2022, and now 6% of all homes in the United States have solar. By 2030, that number is expected to grow to 15%. In 2022, 783 MW of new residential, commercial and community solar capacity deployed was paired with energy storage systems, a new record. By 2027, 33% of new residential solar capacity and 20% of new commercial and community solar capacity will be paired with storage.
California, Texas, and Florida were the top three states for new solar capacity additions for the third consecutive year, with California taking back the top spot after Texas led the nation in 2021. Over 1.8 GW of new solar module manufacturing capacity came online in the U.S. in 2022, bringing total domestic manufacturing capacity to 9 GW. Incentives in the IRA have sparked several new solar manufacturing investments that will bring total domestic capacity to 25 GW by the end of 2023 if all the announcements materialize.
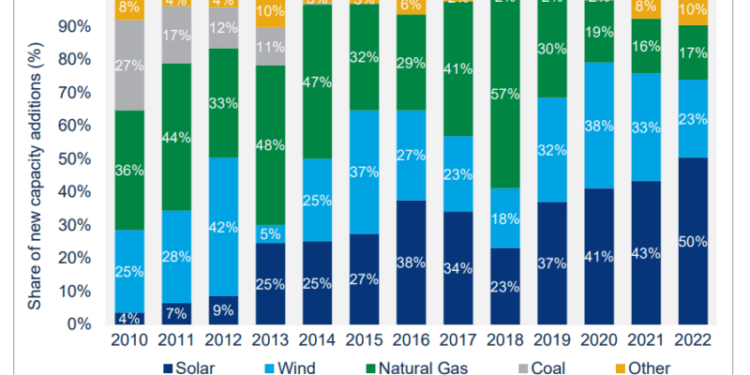
Despite the decrease in new solar capacity additions in 2022, projections for this and next year show a broad market recovery with growth across all sectors averaging 19% per year until 2027. Solar accounted for 50% of all new electric generating capacity additions in 2022, and today it accounts for nearly 5% of U.S. electricity generation. With major uncertainties ahead of the industry, the high- and low-case scenarios can help the industry benchmark potential outcomes. In each scenario, there is roughly 20 GW of upside or downside risk over the next five years — the same amount of capacity installed last year.
FAQ
Q1. How electric car batteries work?
A1. Electric car batteries are typically lithium-ion batteries that store energy and power the motor. They are recharged by plugging the car into an electric outlet or charging station.
Q2. What electric car has the longest range?
A2. The Tesla Model S has the longest range of any electric car currently on the market, with a range of up to 370 miles on a single charge.
Q3. How electric car batteries are recycled?
A3. Electric car batteries are recycled by breaking them down into their component parts and then separating out the metals, plastics, and other materials for reuse. The metals are melted down and reused in new products, while the plastics and other materials are recycled into new products.