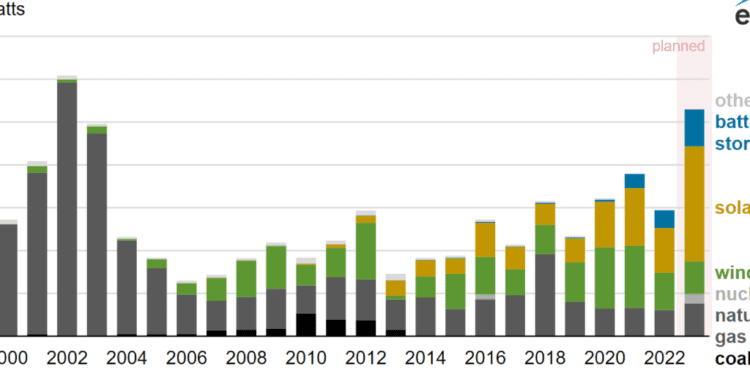
The growth of wind, solar, and battery storage as sources of new electric-generating capacity in the United States is remarkable. In 2023, these three technologies are expected to account for 82% of the new utility-scale generating capacity that developers plan to bring online. This is a huge shift from just a decade ago, when solar and wind capacity were negligible.
The cost of solar panels has dropped substantially, and state and federal policies have introduced generous tax incentives, leading to a boom in solar capacity. As of January 2023, 73.5 gigawatts (GW) of utility-scale solar capacity was operating in the United States, about 6% of the U.S. total. This year, developers plan to add more than half of the new U.S. generating capacity expected in 2023, making it the most U.S. solar capacity added in a single year.
Wind capacity has also grown significantly in the past decade due to lower turbine construction costs, tax incentives, and renewable energy targets. As of January 2023, 141.3 GW of wind capacity was operating in the United States, about 12% of the U.S. total. Developers plan to add another 7.1 GW in 2023. The majority of U.S. wind capacity is located in the central part of the country, but offshore wind farms along the coastline offer significant potential for future growth.
Battery storage systems are increasingly being installed with wind and solar projects to store electricity for later use. In 2023, developers plan to add 8.6 GW of battery storage power capacity to the grid, which would double total U.S. battery power capacity.
Despite the growth of renewable energy sources, they still only account for 17% of the country’s utility-scale capacity and 12% of our electricity production. However, with continued investment and policy support, these numbers are sure to increase in the coming years.
FAQ
Q1. How electric car batteries work?
A1. Electric car batteries are typically lithium-ion batteries that store energy and power the motor. They are recharged by plugging the car into an electric outlet or charging station.
Q2. What electric car has the longest range?
A2. The Tesla Model S has the longest range of any electric car currently on the market, with a range of up to 370 miles on a single charge.
Q3. How electric car batteries are recycled?
A3. Electric car batteries are recycled by breaking them down into their component parts and then separating out the metals, plastics, and other materials for reuse. The metals are melted down and reused in new products, while the plastics and other materials are recycled into new products.