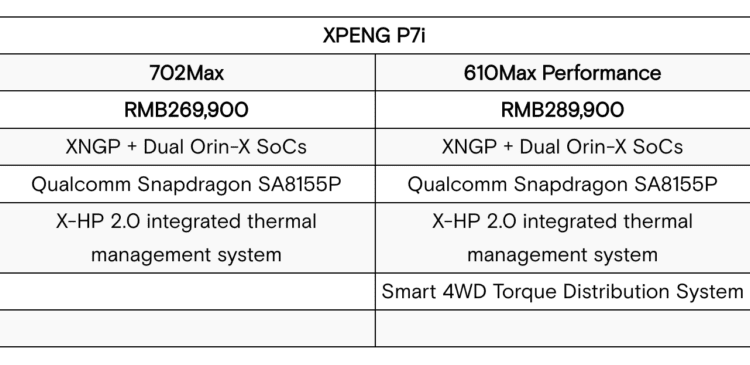
Chinese EV startup XPeng has just released their latest model, the P7i. This model is only available in China at the moment, but it’s already making waves with its good looks, sporty specs, and robust features. The cost of the P7i starts at just RMB249,900 ($36,185), making it an attractive option for those looking for a reliable electric vehicle.
The P7i comes with XPeng’s proprietary XNGP architecture, which is the industry’s most advanced all-scenario driver assistance system. It’s capable of performing City NGP (Navigation Guided Pilot), enhanced Highway NGP and LCC (Lane Centering Control) functions, as well as the industry’s first mass-produced cross-level parking assistance VPA (Valet Parking Assist). It’s powered by a 31-sensor architecture with an enhanced 360° perception capability, designed to achieve L4 ADAS functions in certain scenarios.
The P7i also boasts impressive specs, including up to 757 NM of torque, 0–100 km/h in 3.9 seconds, up to 702 km (436 million) on a full charge (CLTC rating system), and the ability to add 240 km (149 miles) of range in 10 minutes. It also features a 0.236 Cd and 7.1.4 Dolby Atoms sound system with 20 speakers.
XPeng is also quickly increasing its ultra-fast charging infrastructure in China, with plans to upgrade 180 of its supercharging stations to 480kW ultra-fast charging capability. With all these features and more, the P7i is sure to be a hit in the Chinese market. Whether it will give XPeng the sales boost they need remains to be seen.
FAQ
Q1. How electric car batteries work?
A1. Electric car batteries are typically lithium-ion batteries that store energy and power the motor. They are recharged by plugging the car into an electric outlet or charging station.
Q2. What electric car has the longest range?
A2. The Tesla Model S has the longest range of any electric car currently on the market, with a range of up to 370 miles on a single charge.
Q3. How electric car batteries are recycled?
A3. Electric car batteries are recycled by breaking them down into their component parts and then separating out the metals, plastics, and other materials for reuse. The metals are melted down and reused in new products, while the plastics and other materials are recycled into new products.